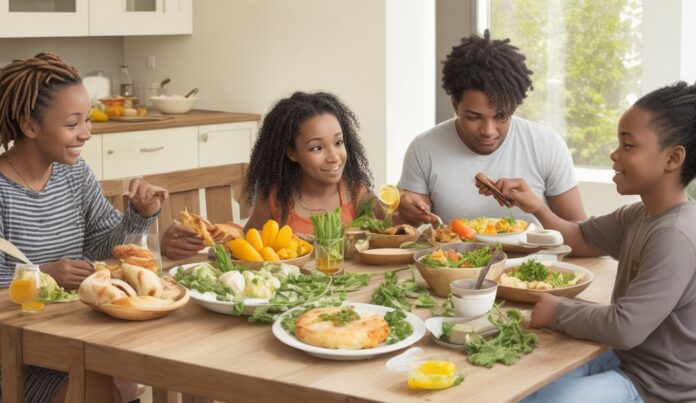
Sustainable diets are becoming increasingly recognized as a key to healthy living and a greener planet. These diets focus on consuming food in a way that meets present nutritional needs while also considering the environmental, social, and economic impacts. Sustainable diets can be defined as eating patterns that promote the health and well-being of individuals, the community, and the planet. According to a study published in the journal Nature, shifting towards sustainable diets can help achieve global nutrition and environmental targets.
The benefits of sustainable diets are manifold. They not only promote personal health by providing a balanced and nutritious diet but also reduce the environmental impact caused by the food system. Sustainable diets also support local and global food systems, ensuring the availability of nutritious food for all while preserving biodiversity.
People Also Read
Key components of a sustainable diet include incorporating more plant-based foods, sourcing food locally to reduce transportation emissions, practicing seasonal eating to support local agriculture, and minimizing food waste.
Sustainable diets play a crucial role in combating climate change. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with food production, conserving water resources, preserving biodiversity, and mitigating land degradation, sustainable diets contribute to a healthier planet and a more stable climate.
Adopting a sustainable diet is not only beneficial for the environment but also for individuals and communities. Practical tips for adopting a sustainable diet include increasing plant-based meals, choosing locally grown and organic foods, minimizing the consumption of animal products, and practicing meal planning and food waste reduction.
By embracing sustainable diets, we can take a proactive approach towards improving our health and the health of the planet, leading to a more sustainable and resilient future.
Key takeaway:
- Sustainable diets promote personal health: Choosing sustainable diets can improve personal health and wellbeing by emphasizing plant-based foods, locally sourced options, and seasonal eating, leading to a balanced diet and overall well-being.
- Sustainable diets reduce environmental impact: Adopting sustainable diets can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve water resources, preserve biodiversity, and mitigate land degradation, contributing to a greener planet.
- Sustainable diets support local and global food systems: Embracing sustainable diets encourages the support of local farmers and food systems, ensuring the availability of nutritious and environmentally-friendly foods for everyone.
What are Sustainable Diets?

Photo Credits: Weightlosteacher.Com by Harold Jones
Sustainable diets: they’re more than just a trendy buzzword. In this section, we’ll dive into what sustainable diets really mean and why they’re essential for both our health and the planet. We’ll uncover the definition of sustainable diets and explore the guiding principles behind them. Get ready to discover how our food choices can make a positive impact on the environment and our well-being. No more compromise between healthy living and a greener planet – sustainable diets hold the key!
Definition of Sustainable Diets
Sustainable diets can be defined as eating patterns that promote both personal health and environmental sustainability. These diets prioritize the consumption of foods that are not only nutritious but also have low environmental impacts. The principles of sustainable diets include focusing on plant-based foods, locally sourced and seasonal ingredients, and minimizing food waste.
By adopting sustainable diets, individuals can experience various benefits. They promote personal health by providing essential nutrients and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Sustainable diets contribute to reducing the environmental impact of food production by conserving water resources, preserving biodiversity, and mitigating land degradation. These diets support local and global food systems by enhancing food security and ensuring the availability of nutritious and culturally appropriate foods.
It’s important to note that the definition of sustainable diets may vary depending on cultural practices, regional contexts, and individual preferences. The common goal remains the same – to nourish our bodies while protecting the planet.
Fact: Sustainable diets have been shown to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to conventional diets.
The concept of sustainable diets, its importance, and its benefits are highlighted in this text. Sustainable diets can be described as eating patterns that prioritize personal health and environmental sustainability. These diets consist of nutritious foods with low environmental impacts, such as plant-based ingredients sourced locally and in season, while minimizing food waste.
Adopting sustainable diets brings various advantages. It improves personal health by providing essential nutrients and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, sustainable diets play a significant role in lessening the environmental impact of food production by conserving water resources, preserving biodiversity, and mitigating land degradation. Moreover, these diets contribute to both local and global food systems by enhancing food security and ensuring the availability of culturally appropriate and nutritious food options.
It should be noted that the definition of sustainable diets can vary based on cultural practices, regional contexts, and individual preferences. However, the overarching goal remains constant: to nourish our bodies while safeguarding the planet.
Fact: Sustainable diets have been proven to decrease greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to conventional diets.
Principles of Sustainable Diets
When considering principles of sustainable diets, individuals can be guided towards making healthier choices for themselves and for the planet. Here are some key principles to keep in mind:
- Environmental sustainability: Sustainable diets aim to minimize the negative impact on the environment. This involves promoting practices such as organic farming, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water resources, and preserving biodiversity.
- Diversity and balance: A sustainable diet emphasizes a variety of foods from different food groups. This promotes nutritional diversity and ensures a balance of essential nutrients.
- Quality and freshness: Choosing fresh, whole, and minimally processed foods is a fundamental principle of sustainable diets. These types of foods often have a higher nutritional value and are less resource-intensive to produce.
- Local and seasonal foods: Prioritizing locally sourced and seasonal foods reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation and supports local farmers and food systems.
- Plant-based focus: Sustainable diets encourage a shift towards plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains. These foods have a lower environmental impact and are associated with numerous health benefits.
- Reduced food waste: Minimizing food waste is a critical principle of sustainability. Planning meals, utilizing leftovers, and composting can help reduce the amount of food that ends up in landfills.
The Benefits of Sustainable Diets

Photo Credits: Weightlosteacher.Com by Daniel Wilson
Discover the many advantages of embracing sustainable diets. From improving personal health to minimizing our environmental footprint and supporting local and global food systems, these diets offer a multitude of benefits. By diving into the realm of sustainable eating, we can make a positive impact on both our own well-being and the health of our planet. So, let’s explore the remarkable advantages that sustainable diets bring to the table.
Promotes Personal Health
A sustainable diet actively promotes personal health by providing essential nutrients, supporting overall well-being, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By prioritizing the consumption of a variety of plant-based foods, individuals can benefit from the abundance of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants they offer, thereby promoting personal well-being. These plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, are not only rich in fiber, which aids digestion and promotes a healthy gut, but also provide essential nutrients such as vitamins A, C, and E, as well as minerals like potassium and magnesium, that are crucial for maintaining optimal health.
In addition to prioritizing plant-based foods, individuals can further enhance their personal health by incorporating locally sourced and organic ingredients into their diets. By choosing to consume fresher produce that is free from harmful pesticides and chemicals, individuals can reduce their exposure to potentially harmful substances while simultaneously improving the nutritional content of their meals.
Furthermore, minimizing the consumption of animal products, especially processed meats and high-fat dairy products, can significantly promote heart health and lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Opting for plant-based protein sources, such as legumes and tofu, provides a healthful alternative while still supplying essential amino acids necessary for personal health.
Apart from the nutritional aspect, sustainable diets also promote personal health through the practice of meal planning and reduction of food waste. By engaging in meal planning, individuals can maintain a balanced diet, control portion sizes, and limit excessive calorie intake, ultimately contributing to weight management and overall well-being.
By consciously adopting a sustainable diet that emphasizes the consumption of nutrient-rich plant-based foods, utilization of locally sourced ingredients, and reduction of animal product consumption and food waste, individuals can actively promote their personal health. In doing so, we not only cultivate healthier lifestyles but also contribute to the creation of a greener planet for future generations.
Reduces Environmental Impact
Eating sustainable diets has a significant impact on reducing environmental damage by minimizing resource consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. By consciously choosing plant-based foods, individuals can effectively decrease their carbon footprint. Plant-based diets prominently require less land, water, and energy when compared to diets that are rich in animal products. Opting for locally sourced foods not only supports local economies but also helps minimize the environmental costs associated with transportation. Moreover, embracing seasonal eating further diminishes the necessity for long-distance shipping and reduces the energy required for food preservation. Minimizing food waste is another crucial aspect to consider as wasted food contributes to greenhouse gas emissions originating from landfills. By consciously planning meals and reducing food waste, individuals can actively contribute to a more sustainable food system. The adoption of sustainable diets plays a crucial role in mitigating environmental damage and promoting a greener planet.
Supports Local and Global Food Systems
- Reduced food miles: Choosing locally sourced foods supports local and global food systems by supporting local farmers and reducing the distance that food travels from farm to plate. This helps to minimize carbon emissions associated with transportation and supports local economies.
- Preserving food cultures and traditions: Consuming locally grown and culturally significant foods supports local and global food systems by helping preserve traditional food practices and heritage. This supports local farmers who grow these varieties and contributes to the cultural richness of communities.
- Fostering agricultural diversity: Prioritizing locally produced and diverse foods supports local and global food systems by promoting biodiversity in agriculture. This includes supporting small-scale farmers who grow a wide range of crops, contributing to the resilience of the food system.
- Ensuring food security: By supporting local and global food systems, sustainable diets contribute to food security by reducing dependence on a few major crops or food sources. This helps to diversify food options and ensures a more stable and accessible food supply for all.
- Supporting fair trade practices: Choosing foods that are produced through fair trade practices supports local and global food systems by creating equitable and sustainable relationships between producers and consumers. This supports local farmers and ensures fair wages and working conditions.
By embracing sustainable diets that support local and global food systems, we can contribute to a greener planet, support local communities, and promote a more resilient and diverse food supply for future generations.
Key Components of a Sustainable Diet

Photo Credits: Weightlosteacher.Com by Henry Scott
Discover the building blocks of a sustainable diet, where every bite counts towards a healthier you and a greener planet. We’ll dive into the key components that make up this eco-conscious eating approach. From embracing plant-based foods to being mindful of locally sourced and seasonal ingredients, we’ll explore ways to reduce our carbon footprint. Together, let’s learn how to minimize food waste and make a positive impact on our environment, one nourishing choice at a time.
Plant-Based Foods
Plant-Based Foods are an essential component of a sustainable diet, as they offer numerous benefits for personal health and the environment. By incorporating more Plant-Based Foods into your meals, you can make a positive impact on both your well-being and the planet.
| 1. Health Benefits | Eating Plant-Based Foods can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. These foods are generally low in saturated fats and cholesterol and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which promote overall good health. |
| 2. Environmental Benefits | Plant-Based Foods have a lower carbon footprint compared to animal-based foods. Producing Plant-Based Foods requires fewer resources, such as water and land, and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing Plant-Based options helps to conserve natural resources and reduce environmental degradation. |
| 3. Biodiversity Preservation | Supporting Plant-Based diets helps protect biodiversity. Animal agriculture is a major contributor to deforestation, habitat loss, and species extinction. By shifting towards Plant-Based Foods, we can help preserve ecosystems and the diverse range of plants and animals that inhabit them. |
| 4. Animal Welfare | Choosing Plant-Based Foods is a step towards promoting ethical treatment of animals. Animal agriculture often involves intensive farming practices that may compromise animal welfare. By reducing or eliminating animal products from our diets, we can contribute to a more compassionate approach to food production. |
Locally Sourced Foods
Choosing locally sourced foods is essential for adopting a sustainable diet. By opting to consume foods that come from nearby areas, we can effectively reduce our carbon footprint and show support for local farmers and businesses. Here are some reasons why incorporating locally sourced foods into our diets is so beneficial:
- Reduced transportation emissions: Locally sourced foods require significantly less transportation compared to imported or long-distance food products. This not only minimizes greenhouse gas emissions but also contributes to creating a healthier environment.
- Fresher and more flavorful: Since locally sourced foods are harvested close to where they are sold, they are often much fresher and retain higher nutrient levels. This results in better taste and enhanced nutritional value.
- Support for the local economy: When we choose to purchase locally sourced foods, we actively support small-scale farmers and local food producers. This, in turn, helps to boost the vitality of the local economy and fosters a greater sense of community.
- Preservation of farmland: By actively supporting local agriculture, we play a vital role in preserving farmland from being converted into other uses, such as urban development. This is essential for maintaining biodiversity and protecting our natural resources.
- Connection to food sources: By consuming locally sourced foods, we have the opportunity to establish a stronger connection to the origins of our food. This experience allows us to learn about various farming practices and develop a deeper appreciation for the food we eat.
If you are looking to incorporate locally sourced foods into your diet, there are various options available. Consider visiting farmers markets, joining community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, or establishing direct relationships with local farmers. By actively choosing locally sourced foods, we can contribute to a more sustainable food system and promote the well-being of both our health and the planet.
Seasonal Eating
When it comes to adopting a sustainable diet, one important aspect to consider is seasonal eating. This practice involves consuming foods that are in season during a particular time of year. Here are some key points to understand about seasonal eating:
- It promotes freshness: Seasonal foods are picked at their peak ripeness, ensuring optimal flavor and nutritional content.
- It supports local agriculture: By choosing foods that are in season, you are more likely to support local farmers and reduce the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
- It reduces environmental impact: Seasonal eating helps to minimize the need for artificial preservation methods, such as refrigeration or chemical treatments, which are often used to extend the shelf life of out-of-season produce.
- It offers variety: Embracing seasonal eating allows you to enjoy a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and herbs throughout the year, as different foods come into season at different times.
By incorporating seasonal eating into your sustainable diet, you can enjoy the freshest, most flavorful foods while supporting local agriculture and reducing environmental impact.
Minimizing Food Waste
- Plan meals ahead: Planning meals in advance can help in minimizing food waste by only buying the necessary ingredients and using them efficiently.
- Buy only what you need: Avoid overbuying groceries by making a shopping list and sticking to it. This will prevent food from going bad before you have a chance to use it, thus contributing to minimizing food waste.
- Store food properly: Proper storage can extend the shelf life of your groceries, helping in minimizing food waste. Use airtight containers, wrap produce properly, and keep your refrigerator at the right temperature.
- Organize your fridge and pantry: Keep track of what you have and prioritize using items that are closer to their expiration dates, which is important for minimizing food waste.
- Use leftovers creatively: Repurpose leftovers into new meals or use them as ingredients for other dishes. Get creative and experiment with recipes to contribute to minimizing food waste.
- Compost food scraps: Instead of throwing away food scraps, consider starting a compost bin. This will not only reduce waste but also provide nutrient-rich soil for your garden, thus helping in minimizing food waste.
- Educate yourself: Learn about proper portion sizes and cooking techniques to avoid preparing more food than necessary, which is essential for minimizing food waste. This can help you minimize leftovers and reduce food waste.
- Donate excess food: If you have surplus food that you can’t consume, consider donating it to local food banks or charities. This way, you can help others while contributing to minimizing food waste.
- Track and measure: Keep track of the amount of food you throw away regularly. This will help you identify patterns and make better decisions when purchasing and preparing food, ultimately minimizing food waste.
By following these steps, you can play your part in minimizing food waste and contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Role of Sustainable Diets in Combating Climate Change
Sustainable diets are not just about our health but also play a vital role in combating climate change. In this section, we will dive into the tremendous impact of sustainable diets on our environment. From reducing greenhouse gas emissions to conserving water resources, preserving biodiversity, and mitigating land degradation, each sub-section will reveal the power of sustainable diets in creating a greener and more sustainable planet. Get ready to explore the astonishing facts and figures that highlight the undeniable connection between our food choices and the health of our planet.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is a fundamental element of embracing a sustainable diet. By consciously making choices in our food consumption, we can make a significant contribution to the reduction of greenhouse gases.
One effective approach is to prioritize meals that are plant-based. The production of animal products is a major factor in greenhouse gas emissions. By shifting towards a more plant-focused diet, we can substantially decrease our carbon footprint.
Choosing locally grown and organic foods is another way to minimize emissions. Locally sourced foods require less transportation, thereby reducing the energy and emissions associated with long-distance transport. Additionally, organic farming methods generally result in lower emissions compared to conventional agriculture.
Significantly reducing the consumption of animal products can have a profound impact. Animal agriculture is responsible for a substantial amount of methane and nitrous oxide emissions, both of which are potent greenhouse gases. Opting for plant-based alternatives or reducing meat consumption can help mitigate these emissions.
Proper meal planning and food waste reduction also play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Planning meals in advance can help avoid unnecessary food waste, which contributes to methane emissions in landfills. By being mindful of portion sizes and correctly storing leftovers, we can reduce food waste and the emissions associated with it.
Adopting a sustainable diet and actively implementing strategies such as increasing plant-based meals, choosing local and organic foods, minimizing animal product consumption, and reducing food waste are all effective ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By making these changes, we can contribute to a healthier planet for future generations.
Conserving Water Resources
Conserving water resources is a fundamental aspect of embracing a sustainable diet. By consciously choosing what we eat, we can make a valuable contribution to the responsible utilization of water. Here are a few ways to conserve water resources:
- Opt for plant-based foods: Producing meat requires a substantial amount of water in comparison to plant-based foods. By including more fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes in our meals, we can reduce our water footprint.
- Embrace seasonal eating: Consuming foods that are in season reduces the requirement for irrigation, thus conserving water. Additionally, seasonal produce tends to be more delicious and nutrient-rich.
- Minimize food waste: Food waste directly translates to wasted resources, including water. By planning meals, storing food correctly, and utilizing leftovers, we can reduce both wasted water and discarded food.
To underscore the significance of conserving water resources, let’s consider the story of a small-scale farmer in a drought-affected region. Through adopting sustainable farming practices and employing water-saving techniques, they managed to minimize their irrigation needs and optimize water usage. As a result, not only did they preserve water resources in their community, but they also achieved higher crop yields, thereby improving their livelihoods and contributing to a more sustainable food system.
Preserving Biodiversity
Preserving biodiversity is a crucial aspect of sustainable diets. By adopting practices that prioritize biodiversity conservation, we can protect the variety of species and ecosystems that make up our planet’s natural heritage.
- Supporting organic farming: Choosing organic foods helps preserve biodiversity by promoting farming practices that avoid the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This reduces the negative impact on pollinators, insects, and soil organisms.
- Embracing native plant species: Including native plants in our diets encourages biodiversity by supporting local ecosystems. Native plants are adapted to local conditions and provide habitat and food sources for a wide range of animals and insects.
- Reducing food waste: Food waste contributes to biodiversity loss as it leads to the unnecessary production of crops, further depleting resources and causing habitat destruction. Minimizing food waste by planning meals, properly storing food, and using leftovers helps conserve biodiversity.
- Supporting sustainable fishing: Choosing sustainably sourced fish helps protect marine biodiversity. Look for labels such as MSC (Marine Stewardship Council) certification to ensure that the fish is caught using methods that minimize harm to marine ecosystems.
Pro-tip: Incorporate a variety of plant-based foods in your diet as they have a lower environmental impact and contribute to biodiversity preservation. Experiment with incorporating different fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains into your meals for a diverse and sustainable diet.
Mitigating Land Degradation
Mitigating land degradation is a crucial aspect of sustainable diets. By adopting sustainable agricultural practices, we can minimize the negative impacts of food production on land and soil health. One effective strategy is implementing agroforestry, which involves planting trees alongside crops to improve soil fertility and prevent erosion. Practicing crop rotation and intercropping can help maintain soil health and prevent nutrient depletion.
Reducing the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides is another important step in mitigating land degradation. These chemicals can harm soil microorganisms and disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems. Instead, organic farming methods can be employed, such as composting and using natural pest control methods, to promote soil health and biodiversity.
Preserving natural habitats and protecting sensitive ecosystems from degradation is also vital. This can be achieved by adopting sustainable land management practices and avoiding the conversion of natural land into agricultural areas.
By mitigating land degradation, we can ensure the long-term sustainability of our food systems and protect the health of our planet. Embracing sustainable diets that prioritize land preservation and soil health will contribute to a greener future for generations to come. Let’s make conscious choices to mitigate land degradation and create a sustainable food system that nourishes both people and the planet.
Practical Tips for Adopting a Sustainable Diet
Looking to adopt a sustainable diet? This section is packed with practical tips to help you on your journey. From increasing plant-based meals to choosing locally grown and organic foods, we’ve got you covered. Say goodbye to excessive consumption of animal products and hello to mindful meal planning and reducing food waste. Get ready to make healthier choices for yourself and the planet!
Increasing Plant-Based Meals
- To increase plant-based meals in your diet, you can start by replacing meat with plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh.
- Additionally, you should incorporate a variety of whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat pasta into your meals.
- Make sure to add plenty of fruits and vegetables to your plate, aiming for at least five servings per day, in order to increase your plant-based intake.
- Experiment with different cooking methods like baking, grilling, or roasting vegetables for added flavor, which can make plant-based meals more enjoyable.
A true story of someone who successfully increased plant-based meals in their diet is that of Laura, a busy working professional. Laura took the approach of gradually incorporating plant-based meals into her routine. She started by replacing one meat-based meal per week with a plant-based alternative. As Laura discovered new recipes and flavors, she gained confidence in cooking plant-based meals and eventually increased the frequency to three times a week. Not only did Laura notice an improvement in her overall well-being, but she also experienced a sense of satisfaction knowing that her food choices were contributing to a greener planet.
Choosing Locally Grown and Organic Foods
When adopting a sustainable diet, choosing locally grown and organic foods is an important step towards reducing environmental impact and supporting local communities. Here are some key reasons why:
Environmental benefits: Locally grown foods require fewer resources for transportation, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Organic farming practices promote soil health, biodiversity, and minimize the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
Freshness and flavor:Choosing locally grown and organic foods ensures that you are getting foods that are harvested at their peak ripeness, ensuring superior taste and nutritional content. By choosing organic options, you can avoid consuming potentially harmful chemicals and additives.
Supporting local economy: Purchasing locally grown and organic foods helps sustain local farmers and food producers. This strengthens the community, creates jobs, and fosters a resilient and sustainable food system.
Food security: Relying on local food sources enhances food security by reducing dependence on long-distance supply chains. In times of disruptions, such as natural disasters or global crises, having local food systems in place ensures access to fresh and nutritious options.
Preserving farmland: By supporting local farmers through choosing locally grown and organic foods, you contribute to the maintenance of farmland in your region. This helps preserve open spaces, protects wildlife habitats, and maintains the beauty of your surroundings.
When choosing locally grown and organic foods, you make a positive impact on your health, the environment, and the local economy.
Minimizing the Consumption of Animal Products
Minimizing the consumption of animal products is a crucial component of adopting a sustainable diet. By reducing our reliance on animal products, we can positively affect both our health and the environment.
- Health benefits: Lowering the consumption of animal products can significantly lower the risk of various diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and specific types of cancer. Choosing plant-based foods, which are usually lower in saturated fat and cholesterol while being higher in fiber and essential nutrients, contributes to overall better health.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: The consumption of animal products substantially contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, notably methane and nitrous oxide. By consuming fewer animal products, we can contribute to the reduction of these emissions and the mitigation of climate change.
- Preserving water resources: The livestock industry demands substantial amounts of water for animal feed and production. By minimizing the consumption of animal products, we can conserve water resources and alleviate water scarcity concerns.
- Protecting biodiversity: Animal agriculture often leads to deforestation and habitat degradation, posing a threat to biodiversity. By reducing our consumption of animal products, we play a role in preserving natural habitats and safeguarding vulnerable species.
- Reducing land degradation: Livestock farming, especially intensive farming practices, can result in soil erosion and degradation. Shifting to a more plant-based diet can contribute to mitigating land degradation and promoting soil health.
Making conscious choices to minimize the consumption of animal products can positively impact our health, the environment, and the welfare of animals.
Meal Planning and Food Waste Reduction
When it comes to adopting a sustainable diet, meal planning and food waste reduction are essential practices to minimize environmental impact and promote a healthier lifestyle.
- Meal planning: Planning your meals in advance allows you to make conscious choices about the ingredients you use and the portion sizes. It helps in reducing impulsive food purchases and prevents unnecessary food waste.
- Buy only what you need: Before grocery shopping, create a detailed shopping list based on your planned meals. Stick to the list and avoid buying excess food that may go to waste.
- Proper storage: Store your food correctly to prolong its freshness. Use airtight containers and labels to help you keep track of expiration dates and prevent food spoilage.
- Reuse leftovers: Instead of throwing away leftover food, repurpose them into new dishes or incorporate them into your next meal. Get creative and find new ways to use ingredients to minimize waste.
- Compost: If you have unavoidable food waste, consider starting a composting system. Composting not only reduces the amount of waste ending up in landfills but also allows you to create nutrient-rich soil for your garden.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about proper food storage techniques, shelf life guidelines, and safe handling practices. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and reduce both food waste and expenses.
By incorporating meal planning and food waste reduction strategies into your sustainable diet, you can contribute to a greener planet and make a positive impact on your health and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are sustainable diets and why are they important for our health and the environment?
Sustainable diets are food choices that meet our nutritional needs while minimizing the impact on the environment. They are important because they promote both optimal and sustainable health for individuals and contribute to a greener planet. By adopting sustainable diets, we can improve our health and well-being while reducing the harmful environmental effects of our food choices.
What is the relationship between sustainable diets and climate change?
Sustainable diets play a crucial role in addressing climate change. Our current food systems, particularly the production of animal-sourced foods, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental changes. By shifting towards plant-based and planet-friendly foods, we can reduce our carbon footprint and mitigate the impacts of human-induced global warming.
How can adopting a sustainable diet benefit our health?
Adopting a sustainable diet can benefit our health in numerous ways. Plant-forward sustainable diets have been shown to have various health benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. By incorporating more plant-based foods and reducing the consumption of harmful food choices, we can achieve a healthier body and a longer life expectancy.
What practical guidance can I follow to adopt a sustainable diet?
To adopt a sustainable diet, you can start by reducing your meat intake and opting for more sustainable protein sources such as legumes and nuts. Increase your consumption of vegetables and whole grains, and choose minimally packaged products to reduce waste. By making simple changes to your diet, you can contribute to a healthier world and reduce your environmental impact.
How does a sustainable diet contribute to the achievement of planetary targets?
A sustainable diet aligns with the sustainable development goals and helps achieve planetary targets. By reducing the consumption of animal-sourced foods and adopting plant-based alternatives, we can conserve water resources, reduce deforestation, and promote biodiversity. By making sustainable food choices, we contribute to the overall health and well-being of the planet.
How can healthcare workers promote sustainable diets?
Healthcare workers can play a vital role in promoting sustainable diets. By integrating education on sustainable eating habits into standardized study plans and patient consultations, clinicians can provide practical guidance to their patients. They can emphasize the health and environmental co-benefits of sustainable diets and encourage individuals to make healthier food choices for a greener planet.